- Keysight Technologies unveils the results of a global study, conducted by Forrester, entitled “Conquer Testing Complexities with Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI).”
- For this study, Forrester surveyed 406 test decision makers online at companies in Europe, North America, and Asia.
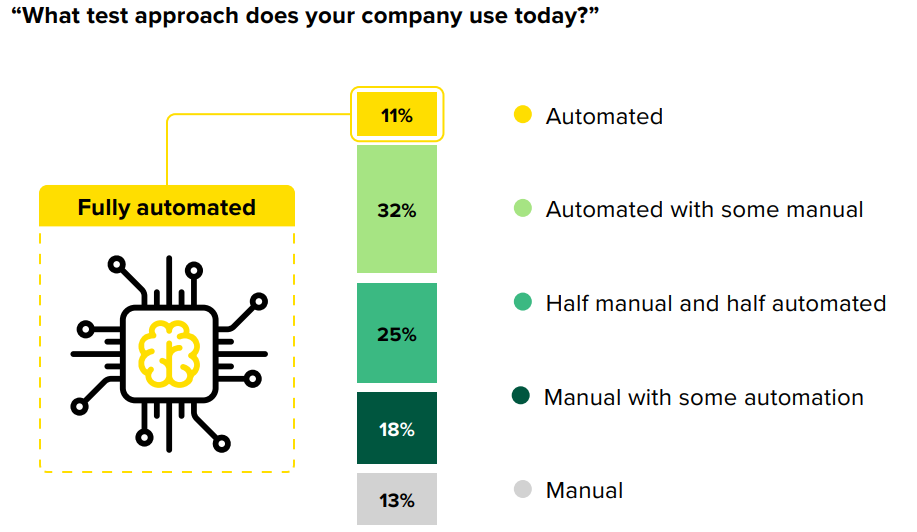
The report reveals that automation is gaining ground and that 75% of companies combine automated and manual testing procedures. However, only 11% deploy a fully automated testing strategy.
“Manual or partially automated strategies are not meeting today’s business needs, and without an AI-based automation strategy, companies will struggle to overcome testing complexity,” observes Jeff Harris, vice president, Portfolio and Global Marketing at Keysight Technologies. In addition, as development teams strive to continue to collaborate remotely, we expect to see an increase in the use of digital twins.”
Among the key technical challenges resulting from test complexity are cycle times, accurate detection of bugs and issues, and then resolving them. These issues directly impact business performance and the product development process. Respondents ranked them in order of importance as follows:
- 51% – The risk of a security breach
- 48% – Increased expenses
- 42% – Slower time to market
- 36% – Defective products
- 34% – Loss of revenue
Companies are finding that manual or partially automated testing strategies are not sufficient to deal with increasing product complexity. As a result, 45% of companies plan to use a fully automated approach in the next three years, a growth of 409%. More than half (52%) said they are looking at AI to integrate complex test suites, a growth of 325%.
Companies expect to gain a variety of benefits from implementing automated testing strategies: increased productivity (59%), the ability to simulate a product’s function or performance (54%), and automating or simulating bug fixing to save time on fix and retest cycles (53%). This is expected to have a number of business implications, including improved product quality to increase customer satisfaction (59%), the ability to reduce time to market (50%), and increased agility in product development cycles (50%).
The survey also found that other technical and operational improvements top companies’ expectations for AI: increased productivity, ability to simulate product operation and performance, and automation/simulation of bug fixing.