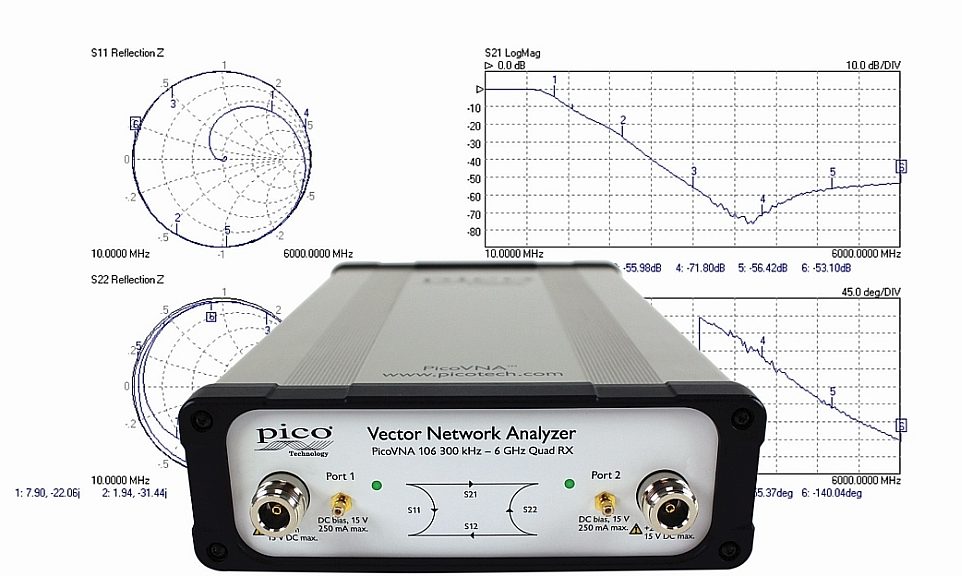
Pico Technology has applied its expertise in compact USB instrumentation to design a modular vector network analyzer that can support developing applications such as 5G, IoT, radar, and tissue and materials imaging. The PicoVNA 106 is an portable, USB-controlled, and laboratory-grade 300 kHz to 6 GHz vector network analyzer.
According to Pico, the PicoVNA 106’s ‘Quad RX’ four-receiver architecture supports both 8 and 12-term calibration without the uncorrectable switching errors, delays and unreliability of traditional three-receiver designs. The instrument supports convenient calibration methods such as ‘enhanced isolation correction’ and ‘unknown thru’.
The PicoVNA 106 has a dynamic range of up to 118 dB at 10 Hz and 0.005 dB RMS trace noise at its maximum bandwidth of 140 kHz. It can gather all four S-parameters at 190 microseconds per frequency point. It can achieve a 500 point 2-port S2P Touchstone file, compatible with test, math, view and EDA simulation tools, in less than a tenth of a second.
Pico have included bias-Ts for the convenient injection of a bias or test stimulus.
The PicoVNA 106 is supplied with Microsoft Windows software to support a range of plot formats for scalar and vector view of dual or single-port parameters. These can be saved or exported in various graphic and tabular formats including Touchstone.
The software includes Fourier transformation to the time domain, adding convenient distance-to-fault capability and pulse response determination. In all cases nominal impedance transformation (10 Ω to 200 Ω) is available, mathematically or using port matching pads, with limit tests on the Cartesian plot formats.
Unwanted measurement contributions from feed lines, probes or test jigs can be eliminated using manual or automatic reference plane offset including, when required, independent offset for each S-parameter.
Alternatively, independent networks can be embedded or de-embedded at each port from a Touchstone representation of each, measured or synthesized. Unusually for any vector network analyzer, embedding or de-embedding is interpolated when measurement and network datasets do not share the same frequency points.
Pico have also included in their free-of-charge PicoVNA 2 software two utilities to tackle gain compression (P1dB) and AM to PM. Both of these use a port power sweep at each test frequency. Both measures are extracted using second-order interpolation.
Pico offers PC3.5 and SMA, male and female test ports via flexible and flex-formable, phase- and flatness-stable test leads. Four mating calibration standards, with traceable data, are assembled into convenient male and female SOLT housings. Like the test leads, the SMA and PC3.5 calibration standards use stainless steel connectors.